
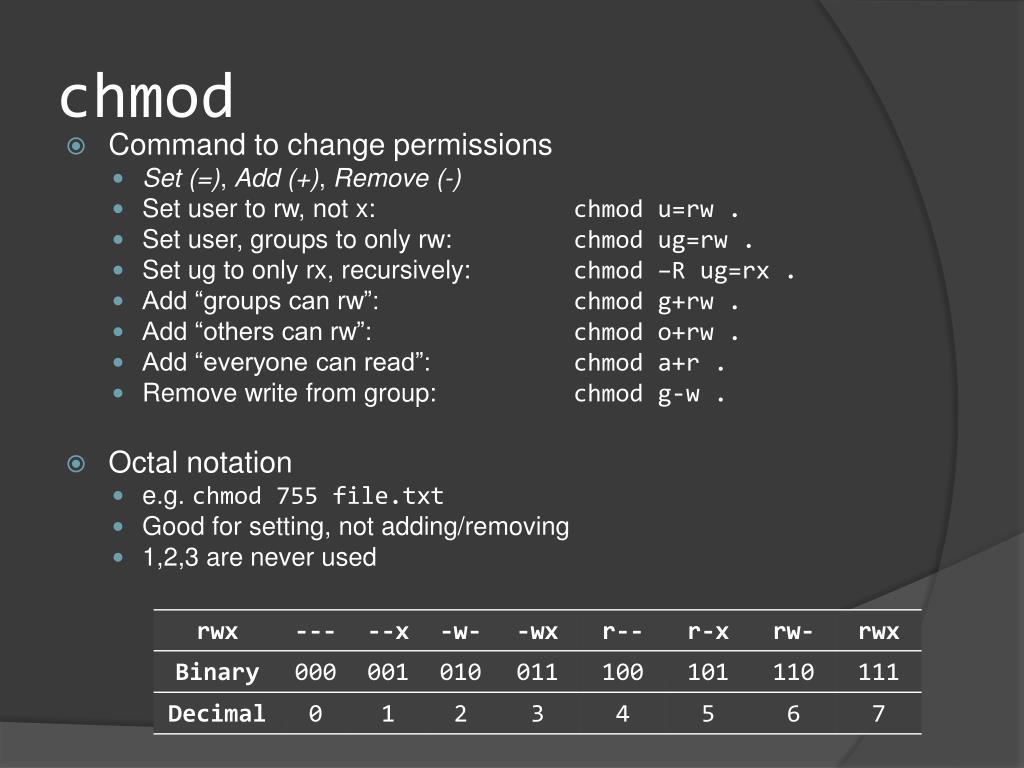
Let us say we have the permission (“r–“). The final three characters show the permissions allowed to anyone who has a UserID on this Linux system. If “r-x” is the second set of 3 characters it means that the members of the group “aditya314” can only read and execute the files. I cannot execute it because it is not a program it is a text file. me) can “read” it (look at its contents) and “write” it (modify its contents). This means that the owner of the file (“aditya314”, i.e. Others – The others permissions apply to all other users on the system, this is the permission group that you want to watch the most.įor example, consider that the user’s permissions for some files is “rw-” as the first three characters. Group – The group permissions apply only to the group that has been assigned to the file or directory, they will not effect the actions of other users.

User – The user permissions apply only the owner of the file or directory, they will not impact the actions of other users. If any of the “rwx” characters is replaced by a ‘-‘, then that permission has been revoked. This permission is given only if the file is a program. The ‘x’ means you can “execute” the file. The ‘w’ means you can “write”, or modify, the file’s contents. The ‘r’ means you can “read” the file’s contents. Each of the three “rwx” characters refers to a different operation you can perform on the file.
The next column shows the size of the file in bytes.In my case I want to give the “aditya314” group of people special access to these files. The next column shows the group owner of the file.In this case it is me, my userID is “aditya314”. The next column shows the owner of the file.The next nine characters (rw-r–r–) show the security we’ll talk about them later.The first character will almost always be either a ‘-‘, which means it’s a file, or a ‘d’, which means it’s a directory.There’s a lot of information in those lines. When you do so, each file will be listed on a separate line in long format. For example, to execute “ls” with the “long listing” option, you would type ls -l You can get more information by using an “option” with the “ls” command. When you execute an “ls” command, you are not given any information about the security of the files, because by default “ls” only lists the names of files. SORT command in Linux/Unix with examples.AWK command in Unix/Linux with examples.Sed Command in Linux/Unix with examples.
LINUX PERMISSIONS RESET HOW TO
How to Change Root Password in Kali Linux?.How to Change the username or userID in Kali Linux?.groupadd command in Linux with examples.Linux Virtualization : Linux Containers (lxc).Linux Virtualization : Resource throttling using cgroups.SetUID, SetGID, and Sticky Bits in Linux File Permissions.ISRO CS Syllabus for Scientist/Engineer Exam.ISRO CS Original Papers and Official Keys.GATE CS Original Papers and Official Keys.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
